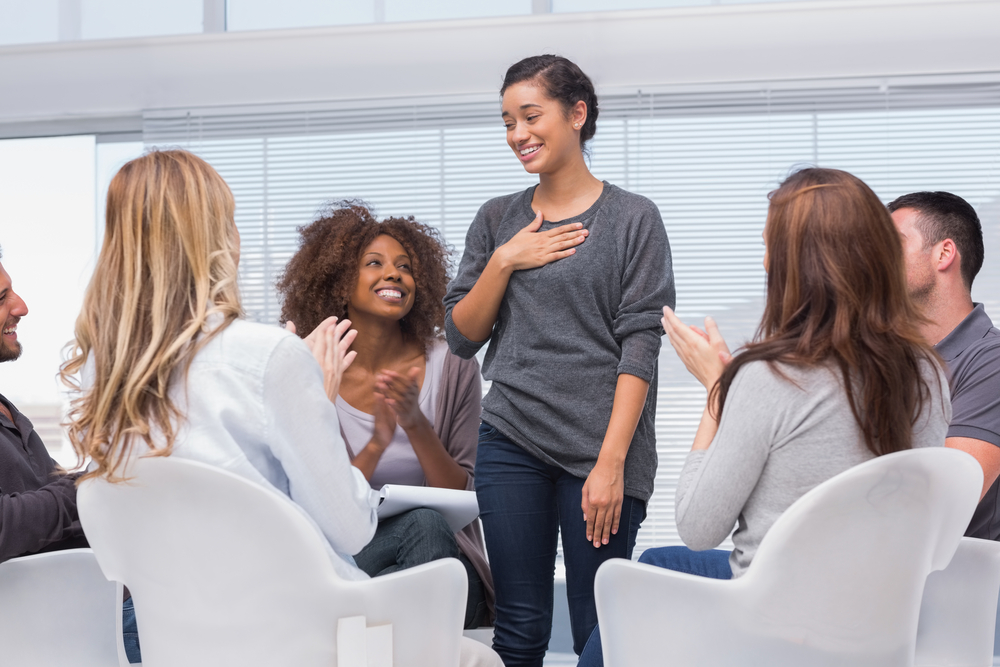
In the realm of healthcare, ensuring the safety and well-being of patients/clients is paramount. However, when it comes to behavioral health, where vulnerabilities may be more complex and nuanced, cultivating a culture of safety becomes even more critical. The Joint Commission (TJC) , Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), DNV Healthcare (DNV), Center for Improving Healthcare Quality (CIHQ), Accreditation Commission for Health Care (ACHC), and CARF all incorporate the tenets of a Safety Culture in their requirements. Safety culture refers to the shared values, attitudes, and practices within an organization that prioritize the protection of patients/clients, staff, and stakeholders from harm. In the context of behavioral healthcare organizations, fostering a robust safety culture is not just desirable – it is essential. Here is why:
Promoting Trust and Transparency
A strong safety culture in Hospitals, Behavioral Health Care and Human Services, and psychiatric hospitals fosters an environment of trust and transparency, where patients/clients feel empowered to seek help and express their concerns without fear of judgment or reprisal. Likewise, encourage staff members to communicate openly about potential risks and errors, facilitating a culture of continuous improvement and learning.
Mitigating Risks and Enhancing Patient Outcomes
Behavioral health settings can be challenging environments, with patients/clients grappling with complex mental health issues and vulnerabilities. By prioritizing safety, organizations can identify and mitigate potential risks, ensuring that patients/clients receive the care they need in a supportive and secure environment. This, in turn, enhances patient outcomes and reduces the likelihood of adverse events.
Supporting Staff Well-being
The well-being of healthcare providers is linked to patient safety. In behavioral health settings, where staff members may be exposed to emotionally demanding situations on a daily basis, prioritizing safety is essential for preventing burnout, compassion fatigue, and other occupational hazards. By fostering a culture that values self-care, resilience, and mutual support, organizations can help safeguard the well-being of their staff and, by extension, the quality of care they provide.
Aligning with Regulatory Standards and Best Practices
Regulatory agencies and accrediting bodies increasingly emphasize the importance of safety culture in healthcare organizations. By prioritizing safety, behavioral health providers can ensure compliance with regulatory and accreditation requirements and demonstrate their commitment to excellence in care delivery. Moreover, embracing best practices in safety culture can help organizations stay ahead of emerging trends and mitigate legal and reputational risks.
Empowering Patients and Families
A robust safety culture empowers patients/clients and their families to actively participate in their care and advocate for their needs. By fostering a culture of collaboration and partnership, behavioral health organizations can build trust and rapport with patients/clients, enhancing engagement and promoting positive treatment outcomes.
Steps for Developing and Maintaining a Culture of Safety
- Top level leadership must demonstrate a visible and unwavering commitment to safety by embedding safety goals into the organization’s mission, vision, values, and business plan
- Initial and ongoing client and staff Culture of Safety assessments are paramount. Utilize surveys, interviews, focus groups, and observations to identify strengths, weaknesses, and improvement priorities
- Foster open communication by encouraging patients/clients and staff to report safety concerns, incidents and near misses without the fear of reprisal
- Provide ongoing education and training on risk assessment, de-escalation techniques, infection control, emergency response protocols, and self-care strategies
- Establish standardized processes and protocols for safety-related procedures, such as patient/client assessments, suicide risk screening, medication management and crisis intervention.
- Empower staff at all levels to hold themselves and others accountable for adhering to safety protocols and promoting a culture of safety in their day-to-day practices.
- Regularly evaluate safety performance data, identify areas for enhancement, and implement targeted interventions. Utilize data analytics, incident reporting systems, and quality improvement initiatives to track progress and measure outcomes.
- Prioritize the well-being of staff and patients/clients by providing resources and support for self-care, stress management, and resilience-building
- Involve patients/clients and their families in safety initiatives by soliciting feedback, sharing information about safety goals and processes, and collaborating on care plans. Empower patients/clients to advocate for their safety and participate in shared decision-making regarding their treatment
- Recognize and celebrate achievements in safety culture improvement. Highlight success stories, acknowledge individuals and teams who contribute to a culture of safety, and celebrate milestones reached in the journey toward a safer organization.
Elements of a Safety Culture Survey Accreditation or Regulatory Survey
Be prepared to discuss the objectives of your safety culture program during an initial or triennial accreditation survey. In fact, Surveyors/Reviewers will review your Safety Culture Survey instrument to determine if your organization’s objectives, and unique needs are reflected in the survey, interview, and focus group questions.
In addition, communicate the purpose, plan, and process for executing your culture of safety program to the surveyor/reviewer during leadership sessions and staff interviews. Concisely present your data to the surveyor/reviewer and emphasize what you have learned from aggregating and analyzing the data. Highlight the interventions you have implemented to continually improve and sustain your performance.
Impact of a High Performing Behavioral Health Safety Culture Program
In the ever-evolving landscape of behavioral healthcare, safety culture is a cornerstone of quality care delivery. By prioritizing safety, organizations can create environments that promote trust, transparency, and well-being for patients/clients and staff alike. As we continue to navigate the complexities of mental health care, it is up to the behavioral healthcare providers to uphold the principles of safety culture as guiding principles for ensuring that all individuals receive the compassionate, high-quality care they deserve.
Remember, safety is not just a goal – it is a journey, and one we must embark on together, every step of the way.
Barrins & Associates Consultation
When we conduct our Mock Surveys and Continuous Readiness Consultations, we always incorporate an evaluation of Safety Culture. We also share our resources on best practices and survey readiness strategies. As always, we will continue to keep you posted on the best solutions for ongoing compliance.
Barrins & Associates – Empowering Patient/Client Safety